Introduction
Shipping code is getting easier everyday with AI. Knowing if your deploys worked, why they slowed down, and how to fix them is hard. GitOps hides most of CD behind commits and controllers. You need clear signals, metrics, events, and logs, mapped to delivery outcomes.
In this post, we’ll wire Argo CD to Parseable, collect telemetry data, and turn it into answers with famous DORA metrics approach.
Quick refresher on DORA metrics
DORA metrics are four key performance indicators developed by Google's DevOps Research and Assessment team to evaluate the performance of software development and delivery processes. They help teams understand how effectively they deliver software and identify areas for improvement. The four DORA metrics are: Deployment Frequency, Change Failure Rate, Time to Restore Service, and Lead Time for Changes.
Tying DORA metrics to Argo CD telemetry
Tie your checks to the four DORA metrics. They frame the “so what?” of CD:
-
Deployment Frequency — How often did you ship? Source: successful syncs per app/env.
-
Change Failure Rate (CFR) — How many deploys fail or roll back? Source: failed syncs + rollbacks vs total.
-
Time to Restore — How fast do you recover from a bad deploy? Source: time from Degraded to next Healthy.
-
Lead Time (CD view) — How fast from merge to production? Source: commit/PR metadata + deploy timestamp.
All the DORA metrics can be tied to below Argo CD signals:
sync_status,health_statusargocd_app_sync_total,argocd_app_sync_duration_seconds_*- Repo request errors, API latencies (
argocd_git_*, server metrics) - Argo roll outs metrics (canary success rate, aborts, step durations)
Setup
Parseable installation
First, deploy Parseable using Docker or Kubernetes following the installation guide. For this setup, ensure Parseable is configured with OTLP ingestion enabled on port 8000. Configure authentication by setting up the username and password that will be used by the OpenTelemetry Collector and other components to securely send data to Parseable.
OpenTelemetry Collector
In this step we create a Collector config that scrapes Argo CD’s metrics ports and exports over OTLP/HTTP to Parseable. Please ensure to adjust service names/ports to your install (common ports shown).
# otel-argocd.yaml
receivers:
prometheus:
config:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: argocd
scrape_interval: 10s
static_configs:
- targets:
- argocd-application-controller:8082
- argocd-server-metrics:8083
- argocd-repo-server:8084
- argocd-commit-server:8087
exporters:
otlphttp/parseablemetrics:
endpoint: "http://parseable:8000"
headers:
Authorization: "Basic YWRtaW46YWRtaW4="
X-P-Stream: argo-metrics
X-P-Log-Source: otel-metrics
Content-Type: application/json
tls:
insecure: true
processors:
batch:
send_batch_size: 8192
timeout: 5s
service:
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers: [prometheus]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlphttp/parseablemetrics]
Deploy the Collector (DaemonSet or Deployment). Pass PARSEABLE_TOKEN as a secret/env and PARSEABLE_HOST. Keep scrape intervals consistent with your alerting windows.
Fluent Bit
We're using Fluent Bit to collect Argo CD logs and forward them to Parseable.
# fluent-bit-argocd.conf
[SERVICE]
Flush 5
Daemon Off
[INPUT]
Name tail
Path /var/log/containers/argocd-*.log
Parser cri
Tag kube.argocd
[FILTER]
Name kubernetes
Match kube.*
Kube_URL https://kubernetes.default.svc
Merge_Log On
# Use HTTP output if you expose a JSON ingest endpoint in Parseable.
# If you prefer OTLP, use the opentelemetry output with /v1/logs.
[OUTPUT]
Name http
Match kube.*
Host parseable.example.com
Port 443
URI /ingest/logs
Format json
tls On
Header X-P-Stream argo-logs
Header Authorization Bearer <TOKEN>
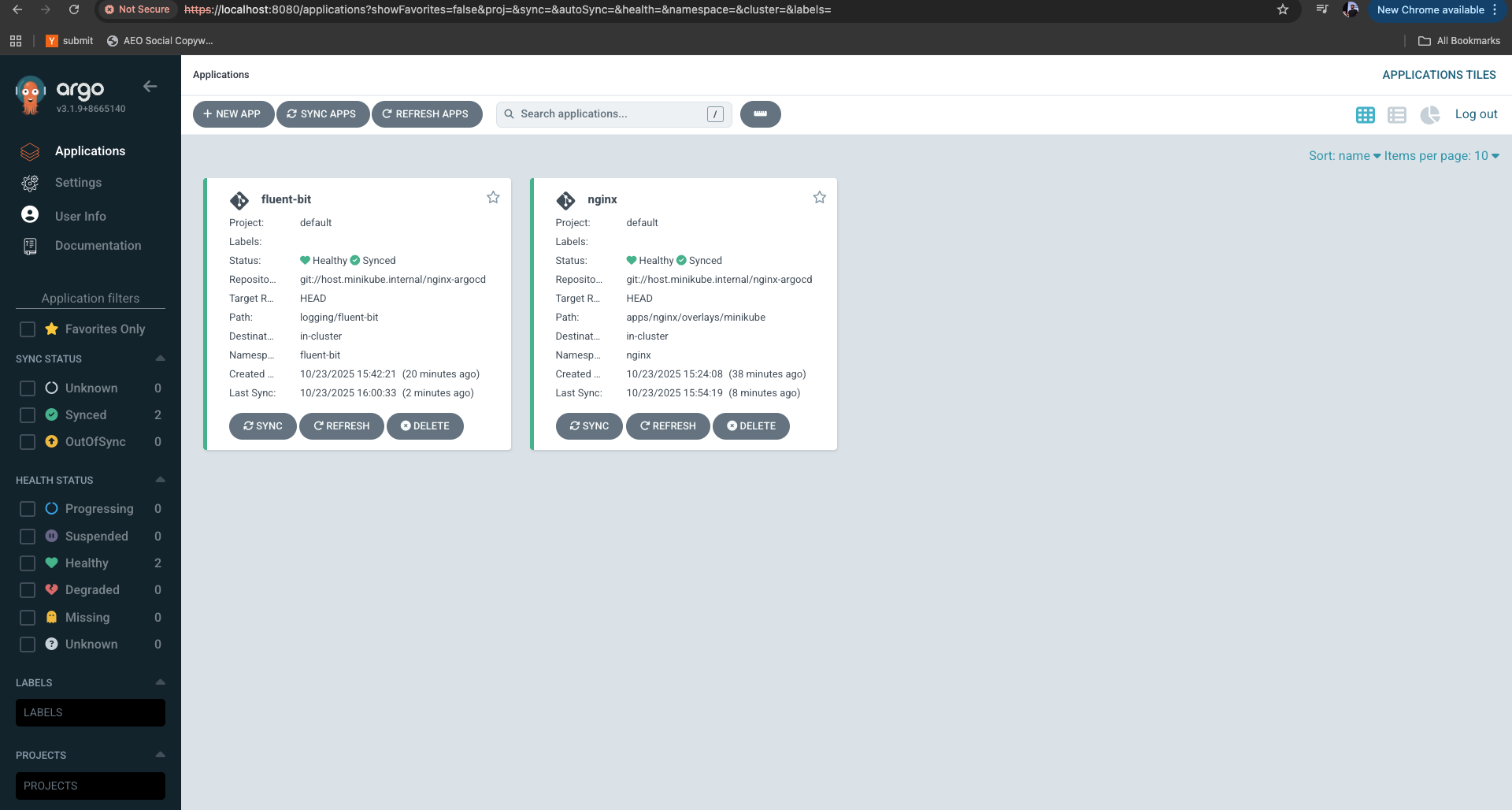
Build dashboards that matter
Now that we have all the data flowing into Parseable, let’s build a dashboard that surfaces the DORA metrics and key Argo CD health signals. Here are the high level topics to cover:
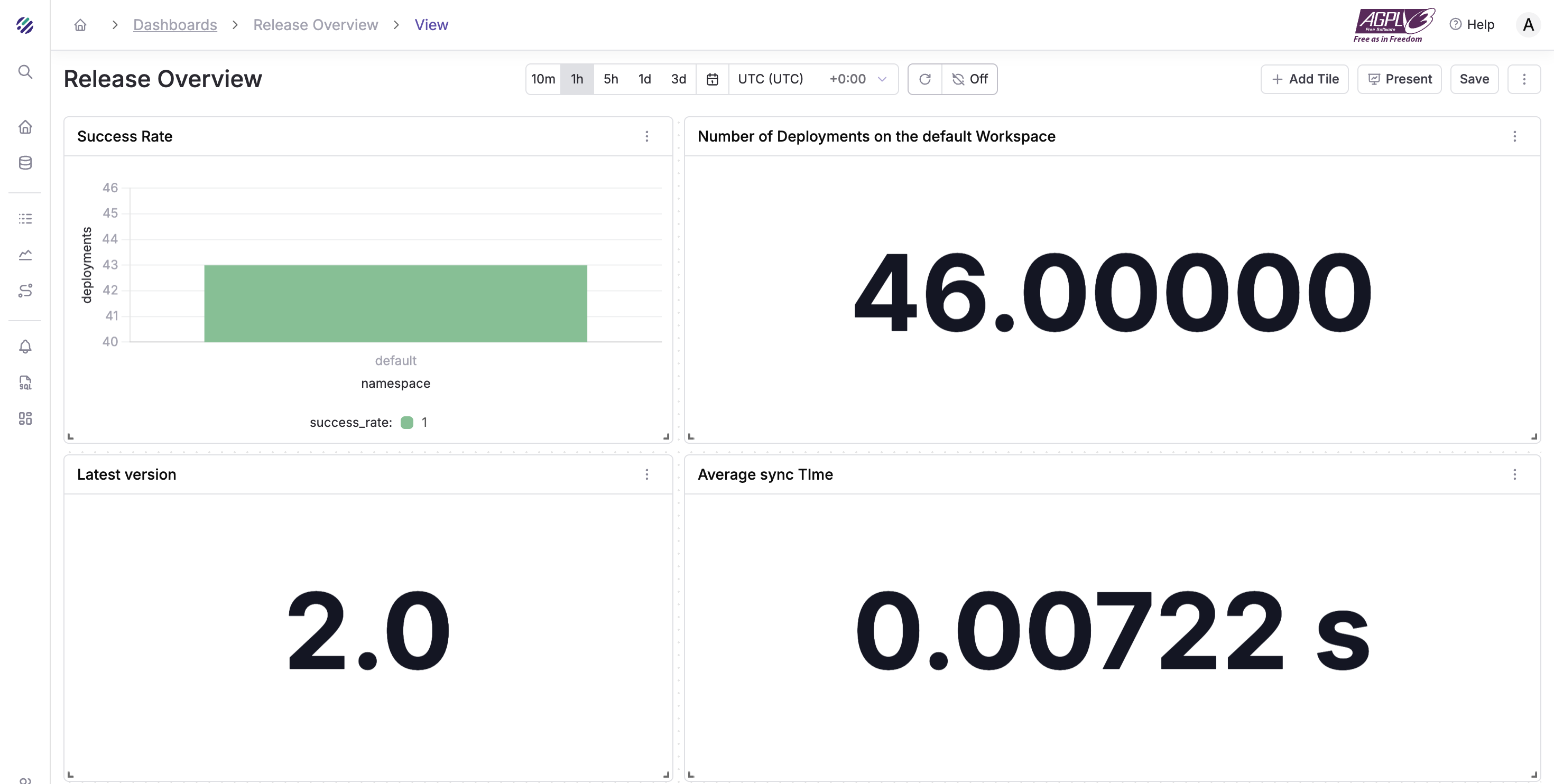
Releases Overview
- Deployments/day
- Success rate
- p95 sync duration
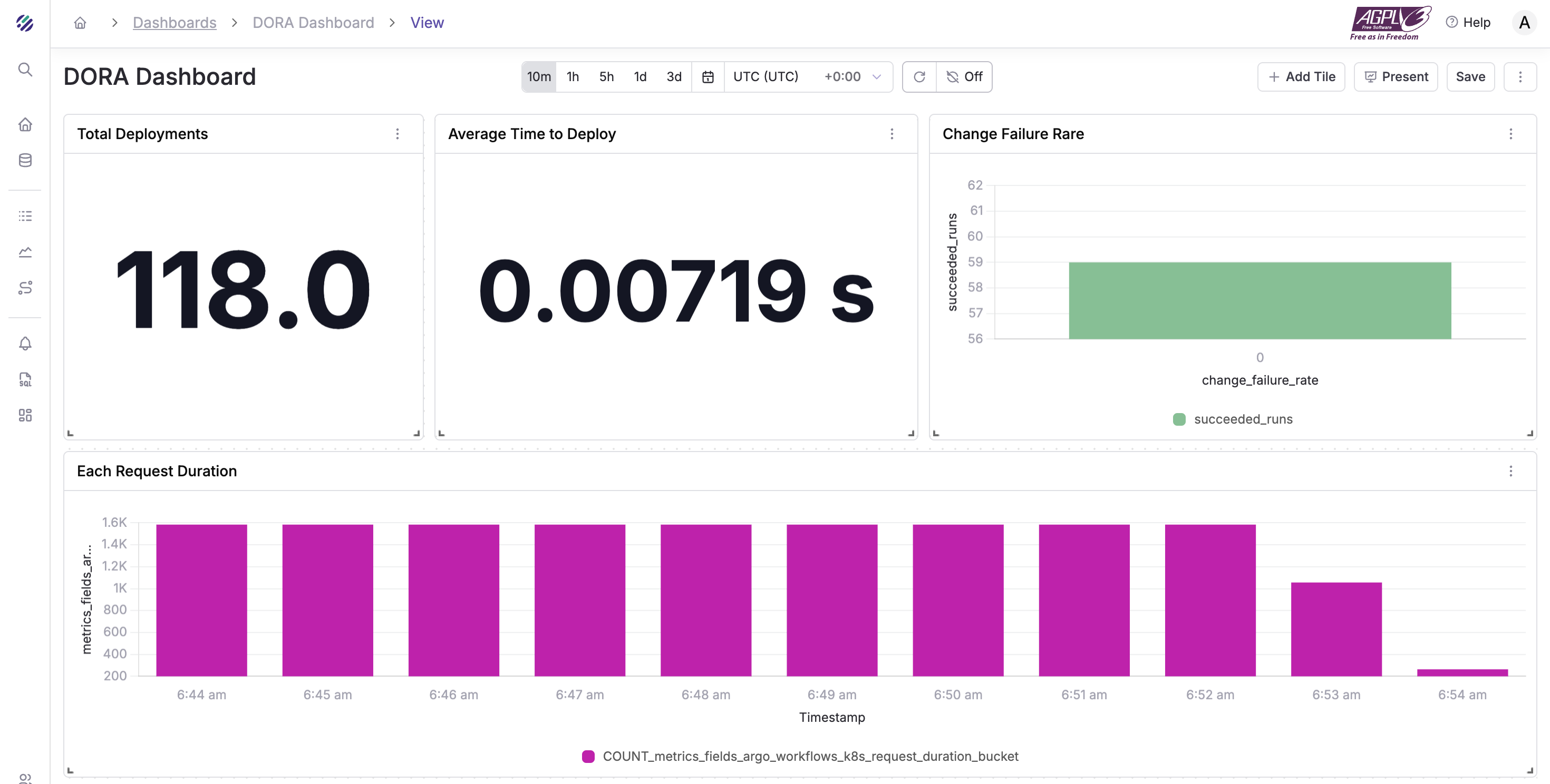
DORA Summary
- Weekly Frequency
- CFR
- Time to Restore (median)
- Simple trend spark lines
Progressive Delivery (if using Argo Rollouts)
- Canary success rate
- Analysis failures
- Aborts by rollout
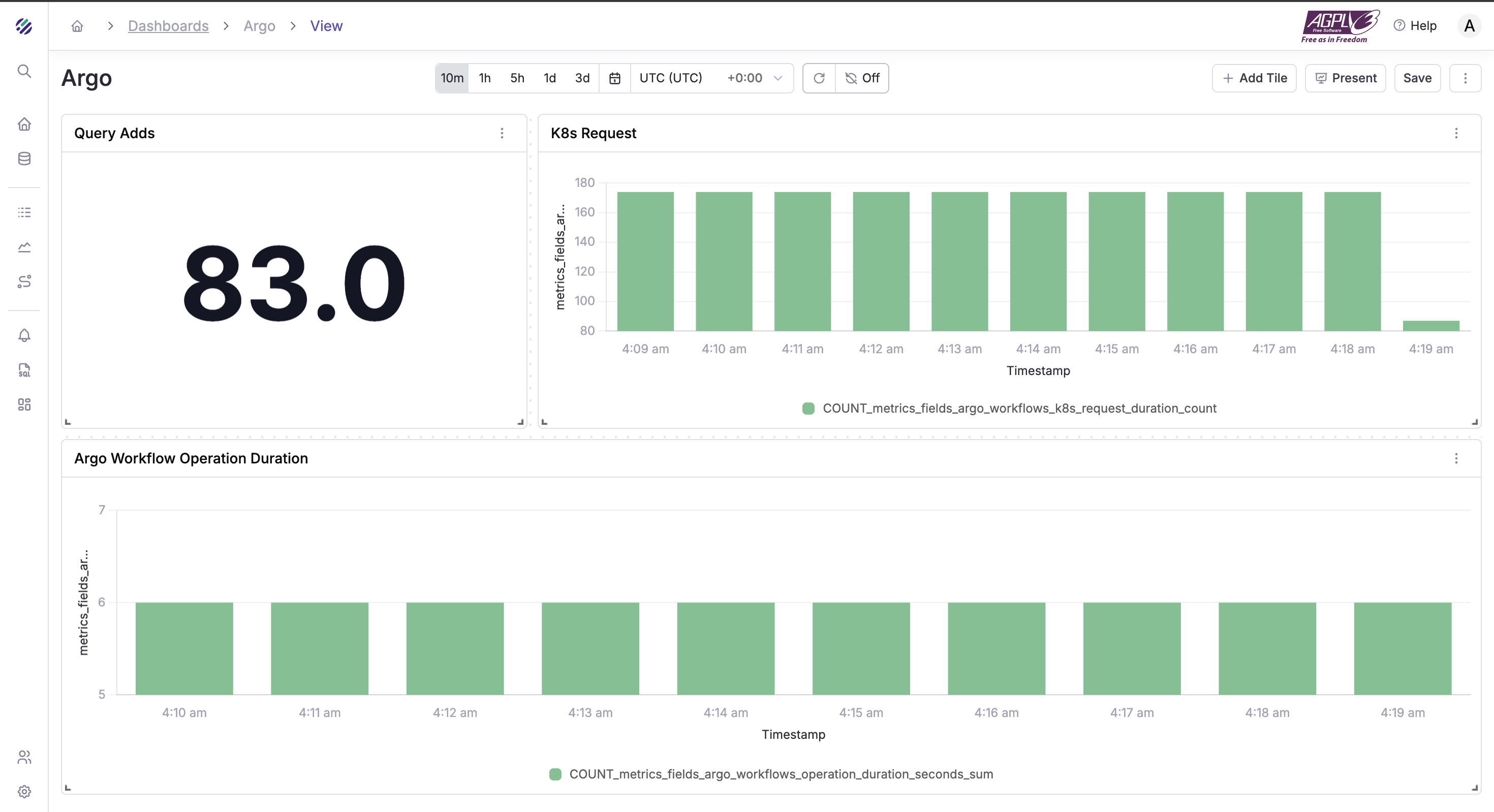
Comprehensive Argo/OTel metrics queries
Below are essential SQL queries for analyzing your Argo CD and OpenTelemetry metrics in Parseable. These queries assume your metrics are stored in the "otel-metrics" stream.
Workflow conditions / phases
SELECT
COALESCE(metrics_tags_phase, 'unknown') AS phase,
SUM(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_workflow_condition) AS wf_count
FROM "otel-metrics"
WHERE p_timestamp > now() - INTERVAL '30 minutes'
GROUP BY COALESCE(metrics_tags_phase, 'unknown')
ORDER BY wf_count DESC;
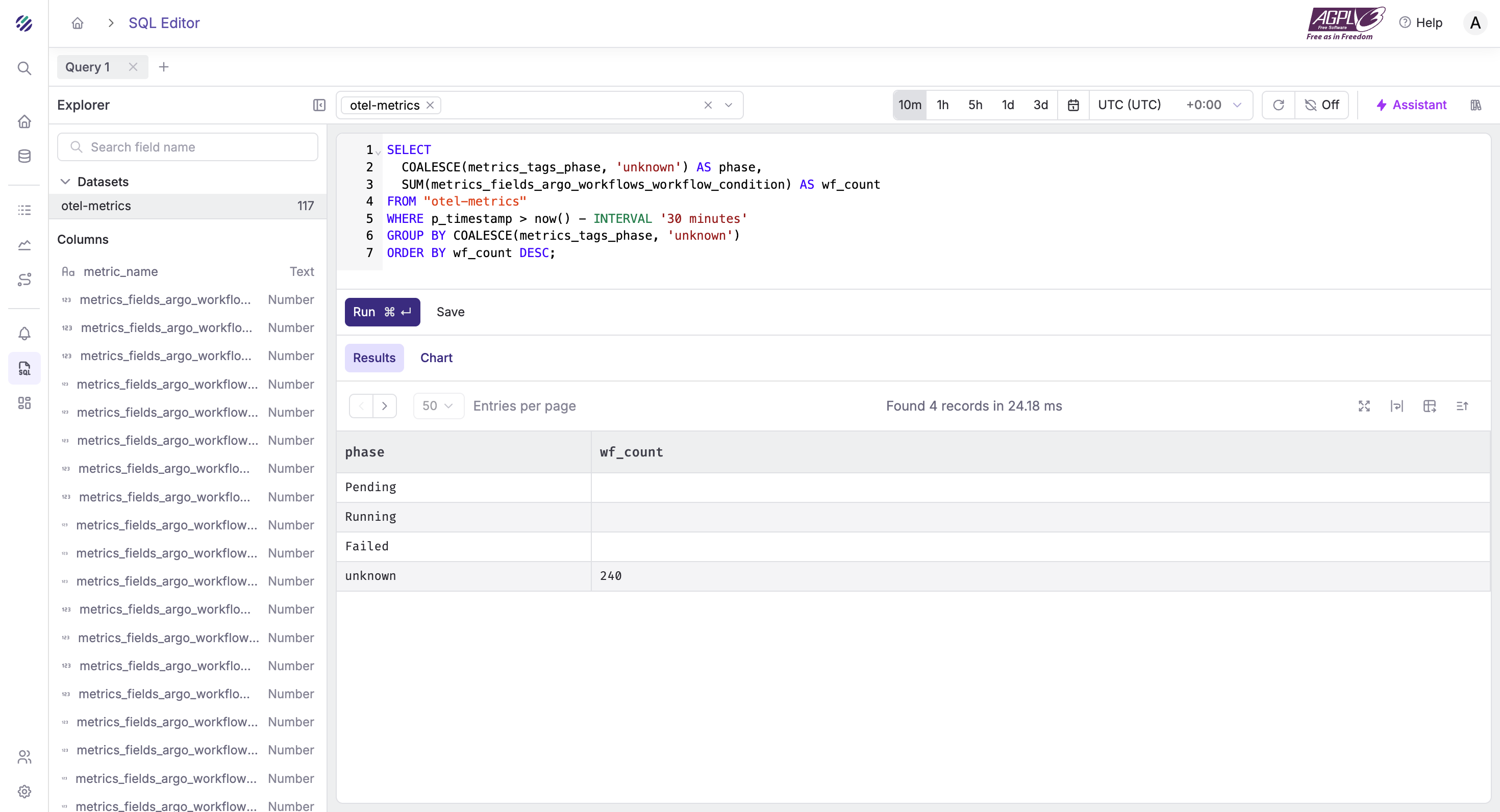
K8s API latency (buckets)
SELECT
COALESCE(metrics_tags_verb, 'ALL') AS verb,
COALESCE(metrics_tags_url, 'ALL') AS url,
metrics_tags_le AS le,
SUM(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_k8s_request_duration_bucket) AS bucket_count
FROM "otel-metrics"
WHERE p_timestamp > now() - INTERVAL '15 minutes'
GROUP BY verb, url, metrics_tags_le
ORDER BY verb, url, le;
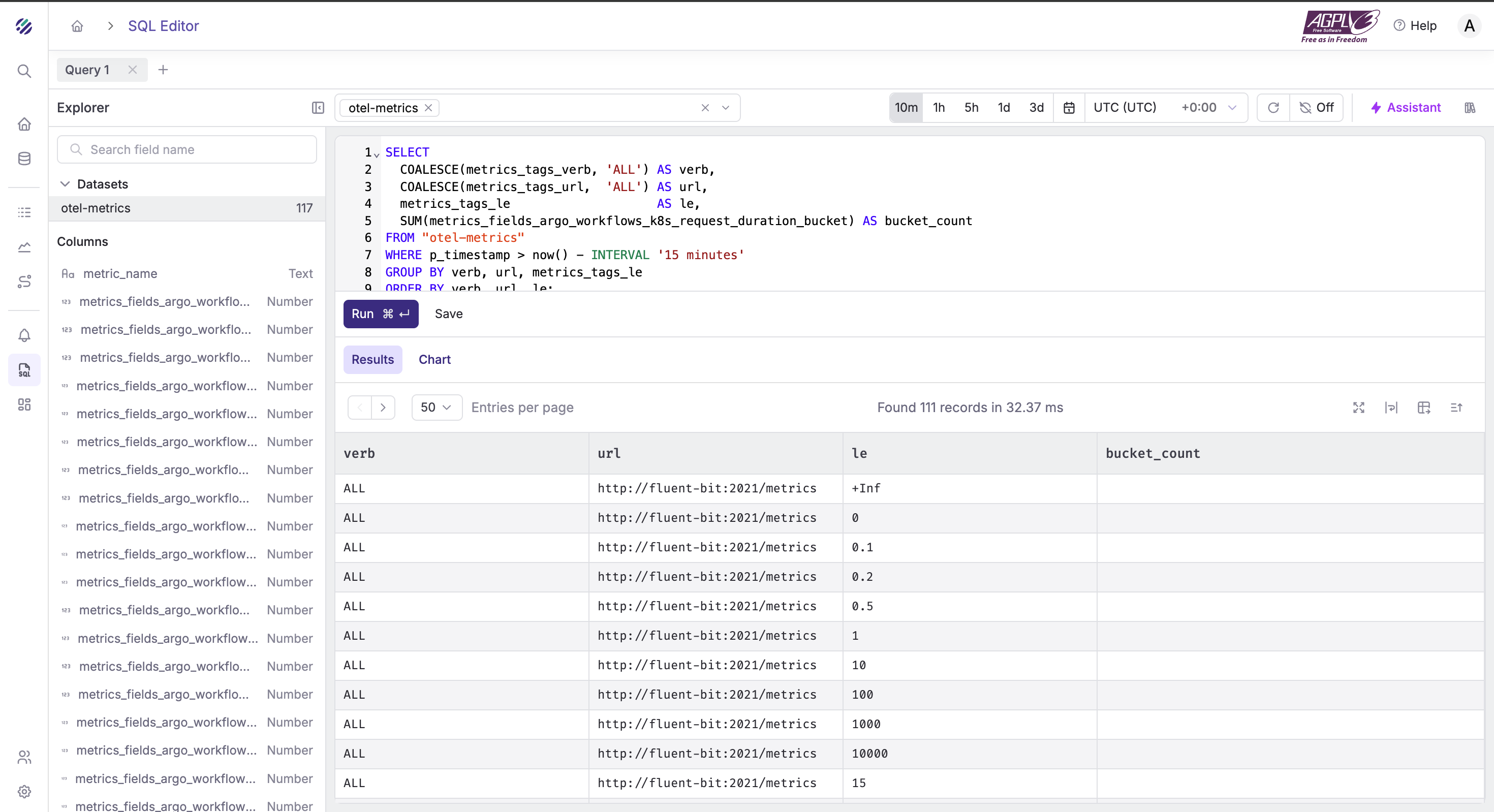
Queue health — depth and unfinished work
SELECT
COALESCE(metrics_tags_queue_name, 'default') AS queue_name,
MAX(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_queue_depth_gauge) AS max_depth,
MAX(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_queue_unfinished_work) AS max_unfinished,
MAX(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_queue_longest_running) AS max_longest_running
FROM "otel-metrics"
WHERE p_timestamp > now() - INTERVAL '15 minutes'
GROUP BY COALESCE(metrics_tags_queue_name, 'default')
ORDER BY max_depth DESC;
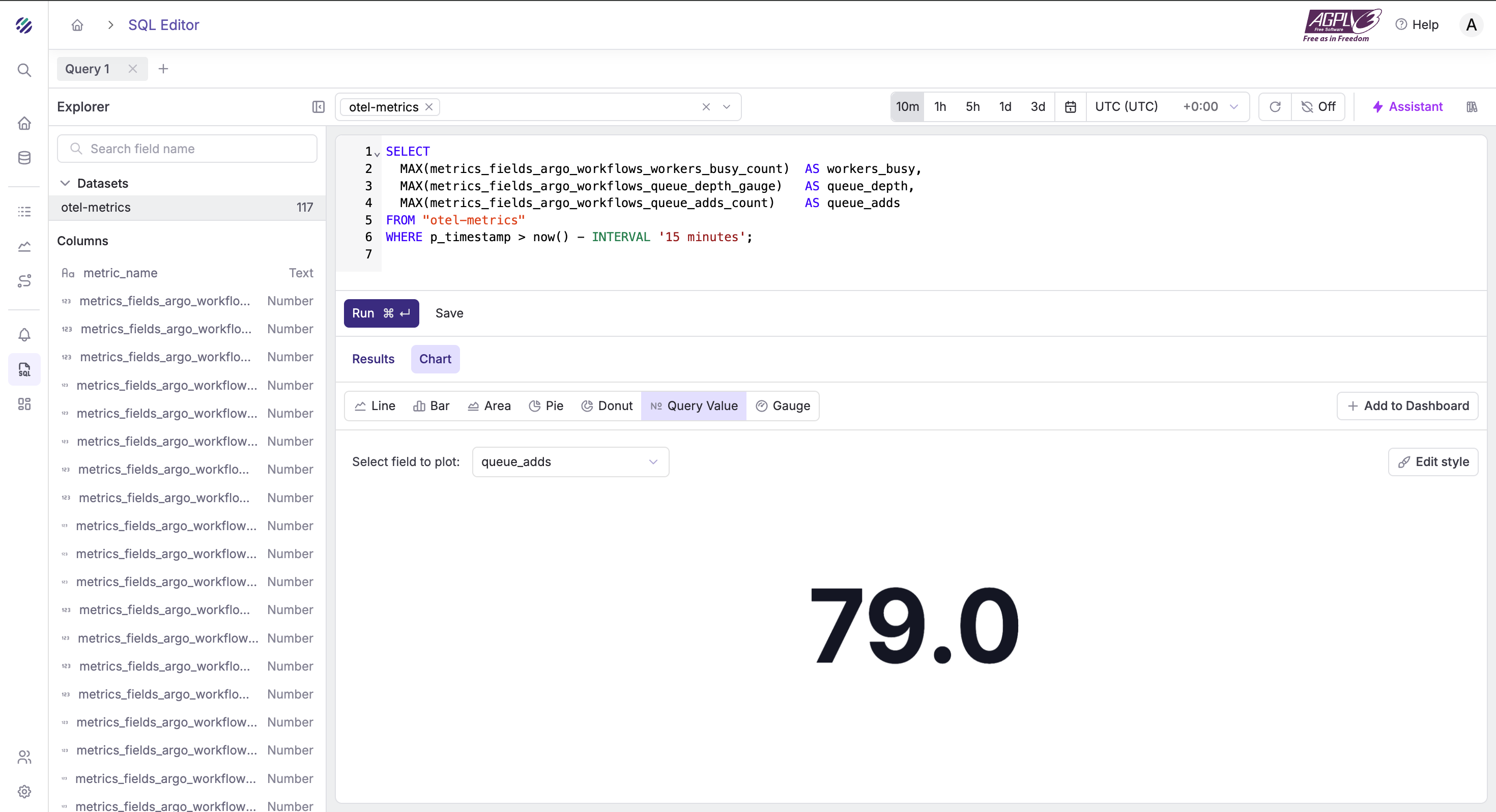
Workers — are we saturated?
SELECT
MAX(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_workers_busy_count) AS workers_busy,
MAX(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_queue_depth_gauge) AS queue_depth,
MAX(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_queue_adds_count) AS queue_adds
FROM "otel-metrics"
WHERE p_timestamp > now() - INTERVAL '15 minutes';
Dropped attributes — to check pipeline hygiene
SELECT
MAX(resource_dropped_attributes_count) AS max_resource_drops
FROM "otel-metrics"
WHERE p_timestamp > now() - INTERVAL '30 minutes';
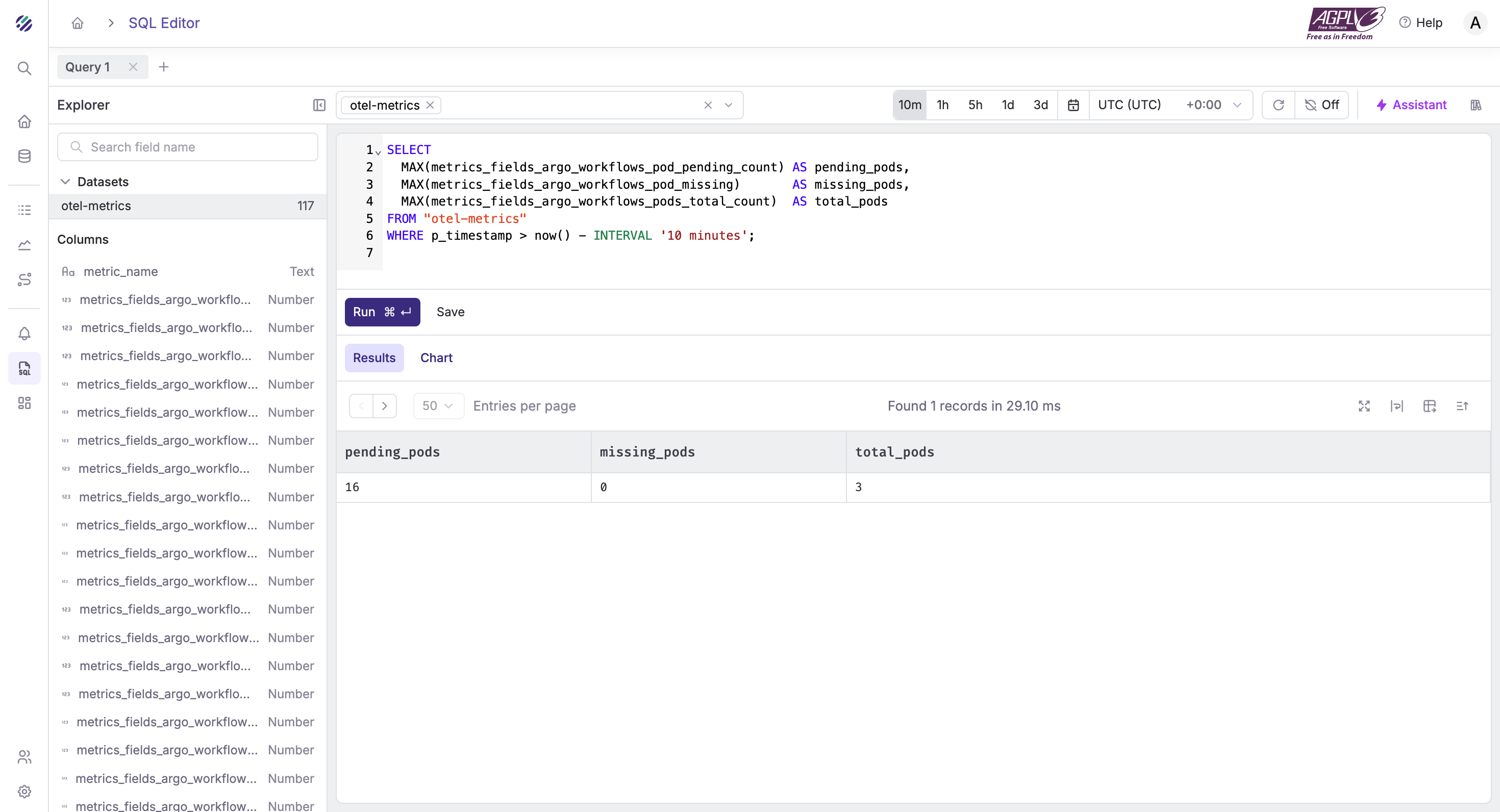
Pods status (pending / missing)
SELECT
MAX(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_pod_pending_count) AS pending_pods,
MAX(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_pod_missing) AS missing_pods,
MAX(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_pods_total_count) AS total_pods
FROM "otel-metrics"
WHERE p_timestamp > now() - INTERVAL '10 minutes';
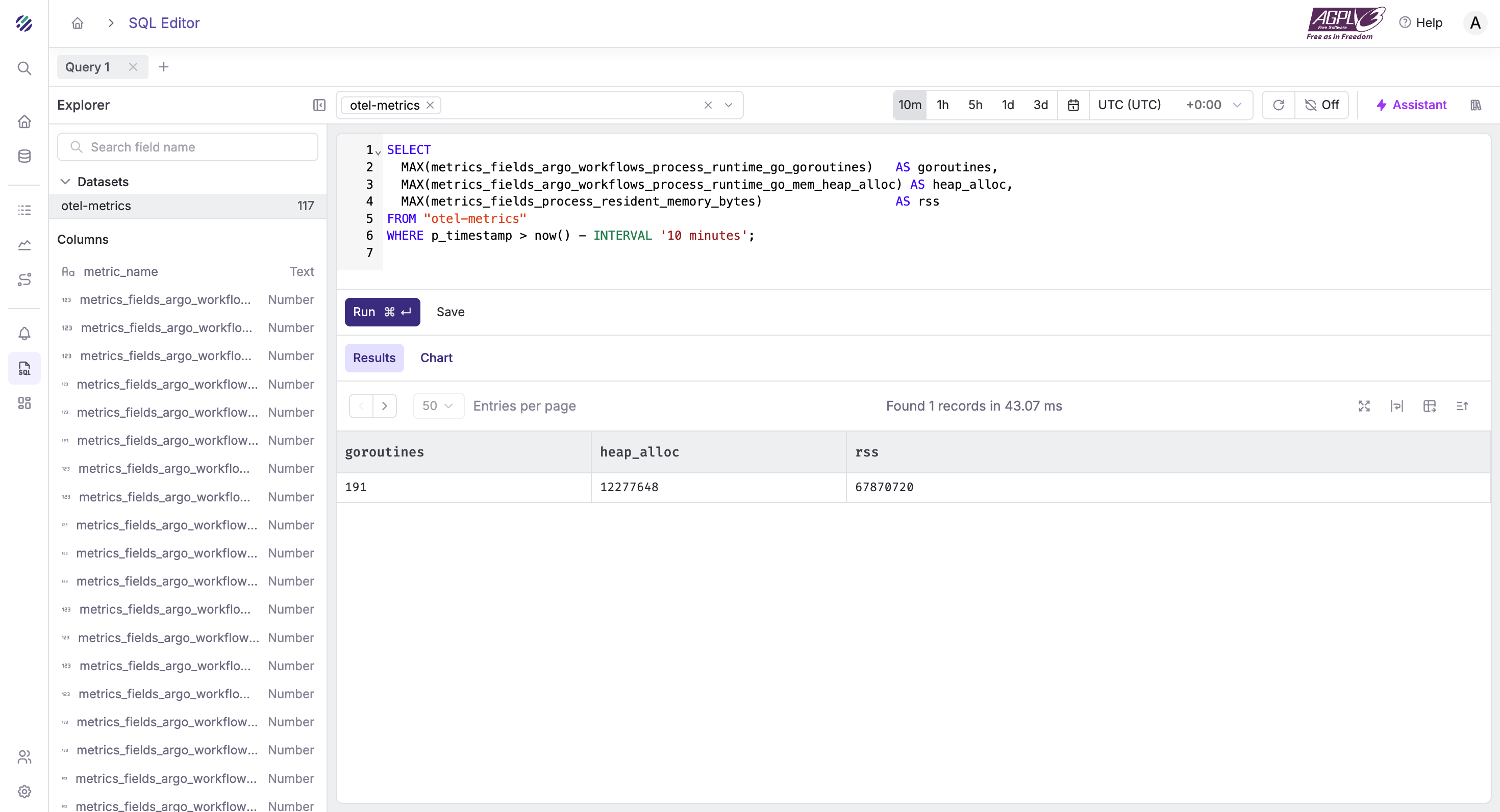
Argo controller runtime / Go health
SELECT
MAX(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_process_runtime_go_goroutines) AS goroutines,
MAX(metrics_fields_argo_workflows_process_runtime_go_mem_heap_alloc) AS heap_alloc,
MAX(metrics_fields_process_resident_memory_bytes) AS rss
FROM "otel-metrics"
WHERE p_timestamp > now() - INTERVAL '10 minutes';
Conclusion
Argo CD already exposes the signals you need. Parseable pulls them into one place, so you can see deployment frequency, spot failures fast, and measure how quickly you recover. Start with metrics and events. Add a handful of focused charts. Wire two or three alerts that actually help.


